The posterior cerebral circulation or simply posterior circulation is the blood supply to the posterior portion of the brain including the occipital lobes cerebellum and brainstem. General anatomy textbooks divide the posterior cerebral artery into three segments.
Arterial Supply To Brain Posterior Cerebral Artery Pca Segments Branches Ranzcrpart1 Wiki Fandom
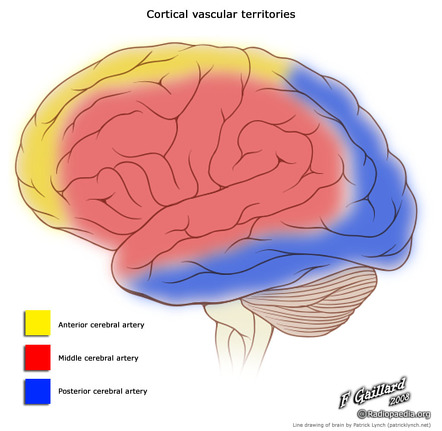
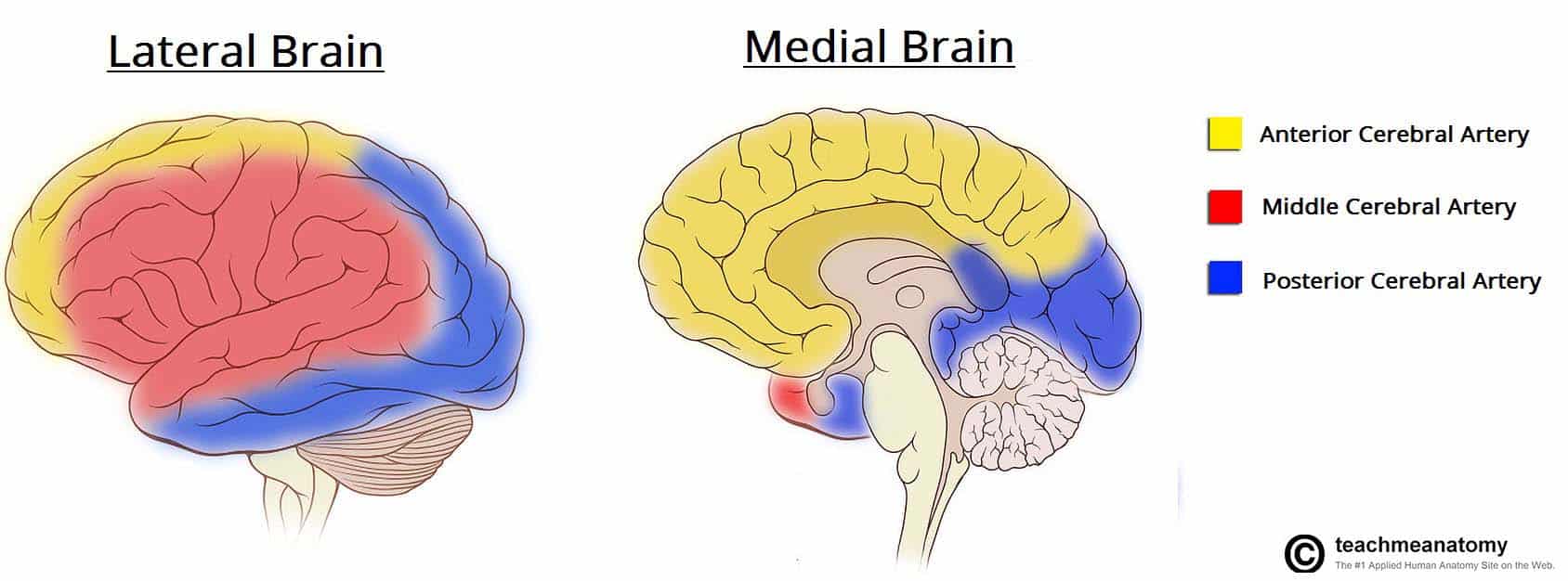
The posterior cerebral artery supplies blood to the back portions of the brain since posterior means back such as the occipital lobe and the.
. It travels within this groove from the. Relay center for descending and ascending information. However the latest neuroanatomical.
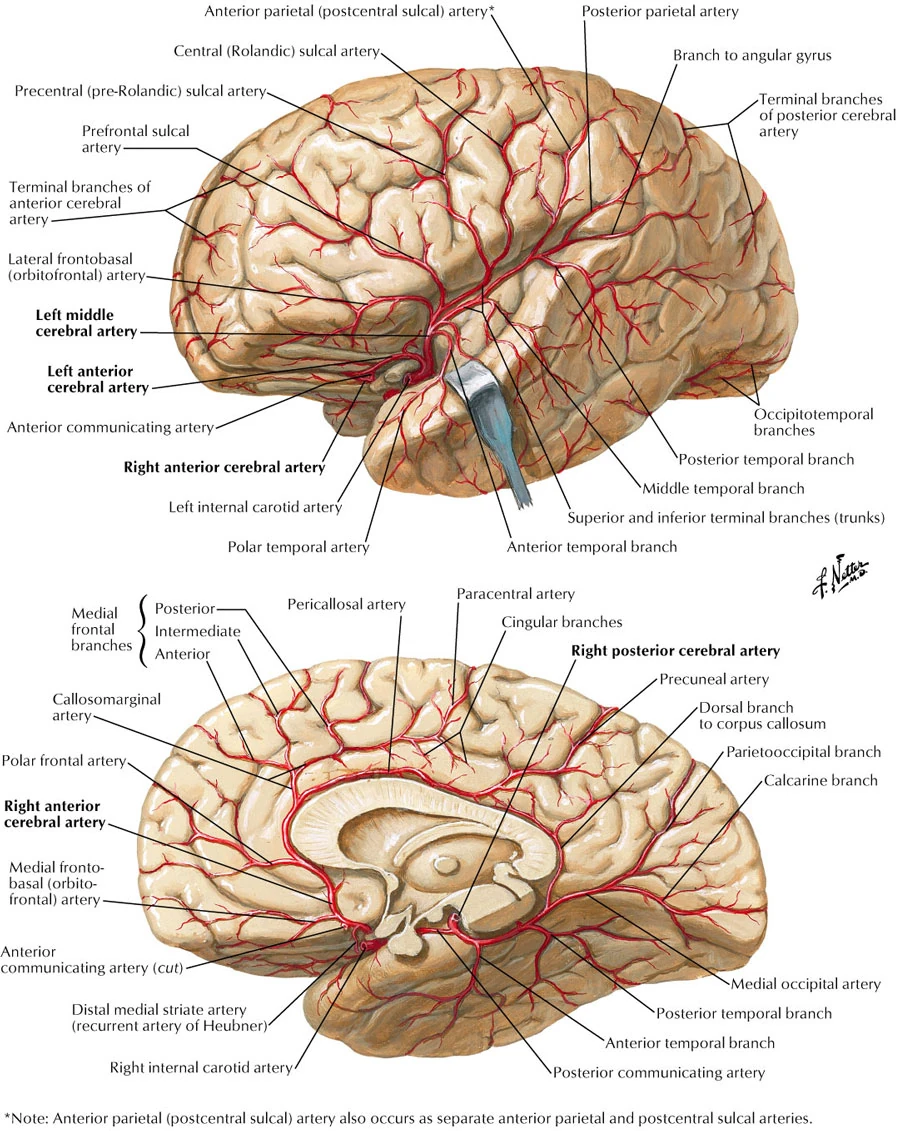
The arteries which comprise the circle are as follows. The anterior cerebral artery the anterior communicating artery the internal carotid artery the posterior cerebral artery the posterior communicating artery and the basilar artery. The Posterior Cerebral Artery PCA supplies the occipital lobe the inferior part of the temporal lobe and various deep structures including the thalamus and the posterior limb of the internal capsule.
It also gives rise to the thalamoperforating vessels. Upon reaching the lateral border of the pons the posterior cerebral artery curves around the cerebral peduncle to reach the medial surface of the cerebral hemispheres where it supplies the temporal and occipital lobes. The Posterior Cerebral Artery PCA supplies the occipital lobe the inferior part of the temporal lobe and various deep structures including the thalamus and the posterior limb of the internal capsule.
The posterior cerebral artery via its cortical branches supplies the inferior and medial surfaces of the temporal and occipital lobes together with a small area on the lateral surface of the hemisphere. Superficial Branch Deep Branch Perfusion Areas Clinical Syndromes PCA Supply 3D THALAMUS. The PCAs supply parts of the midbrain subthalamic nucleus basal nucleus thalamus mesial inferior temporal lobe and occipital and.
The basilar artery runs cranially in the central groove of the pons towards the midbrain within the pontine cistern. Owing to the high oxygen and nutrient demand of the organ it is supplied by two arterial systems. The posterior cerebral artery is part of the Circle of Willis a ring or circle of arteries located at the base of the brain.
The posterior cerebral artery supplies blood to the occipital lobe and is not a cause of cranial nerve deficits. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. The posterior communicating artery supplies blood and oxygen to the brain in instances where the internal carotid or posterior cerebral arteries are blocked.
And the calcarine artery which supplies the visual cortex inferior cuneus and part of the lingual gyrus. This can cause a wide variety of symptoms including vision loss dizziness. Posterior cerebral artery is responsible for supplying blood to the cerebellum brain stem inferior sections of temporal lobes and center of occipital lobes.
About fifteen percent 15 of the daily cardiac output is utilized by the brain. The posterior cerebral artery PCA is one of a pair of arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe part of the back of the human brain. Where is the basilar artery tip.
The middle cerebral artery is the largest branch of the internal carotid. Anterior inferior cerebellar artery AICA which supplies the middle portion of the cerebellum and then the basilar artery gives off the superior cerebellar artery which supplies the superior aspect of the cerebellum The basilar artery finally terminates in the two posterior cerebral arteries PCAs which give off the posterior communicating arteries which. Due to the anastomotic circle of Willis the posterior circulation connects via the posterior communicating arteries to the anterior circulation.
The posterior cerebral artery is susceptible to occlusion a sudden blockage usually resulting from a blood clot. A posterior division includes the two terminal branches of the PCA. The posterior cerebral artery supplies blood to the center of the occipital lobes the inferior sections of the temporal lobes the brain stem and the cerebellum.
The middle carotid artery supplies parts of the brain responsible for movement and feeling in the trunk limbs and face. The posterior cerebral arteries provide blood to the occipital and temporal lobes. Anterior and posterior circulations provide the.
The parietooccipital artery which supplies part of the cuneus and precuneus the superior occipital gyrus and occasionally the precentral and superior parietal lobule. This area contains the calcarine cortex also known as the primary visual cortex. P1 P2 and P3.
The circle of Willis is composed of arteries and crucial to cerebral circulation. A nurse is measuring the BP of a hypertensive obese patient who has been admitted to the hospital for increased blood glucose levels. More often however it keeps going traversing the basilar which has a large diameter and is arrested at the upper.
At the level of the midbrain the basilar artery bifurcates to form the two posterior cerebral arteries PCA. Its first branch is the. Posterior circulation is supplied by the vertebral arteries VA posterior inferior cerebellar arteries PICA basilar artery BA anterior inferior cerebellar arteries AICA pontine branches of the basilar artery superior cerebellar arteries SCA PCA and PCOM.
The posterior cerebral artery curls around the cerebral peduncle and passes above the tentorium to supply the posteromedial surface of the temporal lobe and the occipital lobe. Common neurovascular anatomy. The anterior circuit is supplied by the internal carotid arteries.
It branches off the internal carotid artery. The posterior circuit is supplied by the vertebrobasilar system. If an embolus travels in a vertebral branch it may stop where the vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery.
The smaller branches of posterior cerebral artery transfer blood to midbrain region of the optic path. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system the vertebral arteries provide supply blood to the upper spinal cord brainstem cerebellum and posterior part of brain. The visual cortex responsible for the contralateral field of vision lies in its territory.
3 rows The middle cerebral artery MCA is a terminal branch of the internal carotid artery and is part. This region includes calcarine cortex often known as the primary visual cortex. The posterior cerebral arteries PCAs are paired vessels usually arising from the top of the basilar artery and curving laterally posteriorly and superiorly around the midbrain.
A solid understanding of the pathophysiology of a posterior cerebral artery PCA stroke as well as the syndrome relating to it requires adequate knowledge of the structures and vascular anatomy of the brain.

Posterior Cerebral Artery Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

The Posterior Cerebral Arteries Youtube
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy
Blood Supply Of The Central Nervous System Gross Anatomy Of The Brain Part 2

Posterior Cerebral Artery Wikipedia
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/posterior-cerebral-artery/gVuxrUl1nNuaP7TUBNw3g_A._cerebri_posterior_02.png)
0 comments
Post a Comment